Popular

Innovation examples
HealthToxicology
Zebrafish in toxicity testing
Zebrafish are increasingly recognised as a useful model for toxicity testing of chemical substances. Testing strategies are becoming more based on mechanisms of toxicity structured in adverse outcome pathways describing the chain of events leading to toxicity or disease. Using a battery of dedicated in vitro and in silico assays, insight can be gained in how exposure leads to disease. For certain diseases it is known that toxicity relies on the interaction between different organs and cell types, which requires research on whole organisms in addition to simple in vitro models. The zebrafish is considered a valuable whole organism model in a mechanism-based testing strategy. At RIVM, the zebrafish embryo model is used for testing the effect of chemical substances on several adverse outcomes and diseases.
For more information see: https://ehp.niehs.nih.gov/doi/10.1289/EHP9888; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136717; www.linkedin.com/in/harm-heusinkveld

Innovation examples
HealthIn vitroOrgan-on-Chip
An iPSC-derived blood-brain barrier to model neurodegeneration
The blood-brain barrier is a layer of cells that protects our brain from harmful compounds. However, due to this tight barrier, many drugs to treat neurological diseases cannot enter the brain either.
There are currently no good models to test these types of drugs. Henrique Nogueira Pinto is a PhD candidate at the Vrije Universiteit in Amsterdam. He is developing a blood-brain barrier model coupled to mini-brains. With this model, he aims to more reliably test how drugs can be transported over the blood-brain barrier and what their effect on the brain is.
Click on the info button for the full version of the video. Click here (https://fluidsbarrierscns.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12987-022-00316-0#Sec3) for a review of the current status of in vitro models for the blood-brain barrier.

Questions
HelpathonsHealth
Helpathon #4 - can you help Frank?
Can you help Frank with integrating an immune system into a macaque lung organoid to address local immunity to tuberculosis with his vaccination strategy?
Join Helpathon #4, look at www.tpihelpathon.nl/coming-up !
Frank Verreck does research on tuberculosis at the Biomedical Primate Research Center (BPRC). Tuberculosis is the most deadly infectious disease worldwide! For the past hundred years, BCG (Bacillus Calmette Guérin) vaccinations take place through the skin. Research shows that macaques can be better protected from this infection by vaccination through their lungs. Frank really wants to further study the potential of this alternative vaccination strategy. He wants to understand how this BCG vaccination works in macaques lungs.
Innovation examples
HealthIn vitroOrgan-on-Chip
Stem cell derived Vessels-on-Chip to study brain disorders
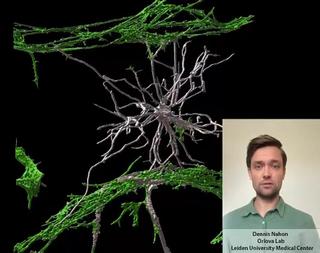
Dennis Nahon is a PhD candidate in the Department of Anatomy and Embryology at the Leiden University Medical Center. In his research, under supervision of Dr. Valeria Orlova (https://www.orlovalab.com/) and Prof. Dr. Christine Mummery, he aims to mimic a blood vessel in the brain by combining different stem cell derived cell types, in a 3D Vessel-on-Chip model. Here, an example of these in vitro blood vessels is shown in which certain brain cells known as astrocytes (in white) interact with the blood vessels (in red). This model paves the way for investigating brain vessels outside the human body, while reducing the need for animal models.

Innovation examples
ToxicologyIn vitroOrgan-on-Chip
Cartilage-on-a-chip for studying joint degenerative diseases
Carlo Alberto Paggi is currently a PhD candidate at the University of Twente in the research group of Prof. Marcel Karperien and Prof. Séverine Le Gac. Karperien’s lab focus on the biological aspects of osteoarthritic research while Le Gac’s specialize in organ-on-chip development. The project of Carlo Alberto is developing a joint-on-chip platform to create a reliable in vitro model to study disease progression in osteo- or rheumatoid arthritis. The model combines different organ-on-chips aimed at replicating each a tissue around the joint such as cartilage, bone and ligaments. This new technology focuses on better reproducing human models and at substituting the use of animal models for drug research. If you want to know something more about the project and the groups, you can follow the link in the video.
Carlo Paggi was nominated for the Hugo van Poelgeest prize for his research on a cartilage-on-a-chip model to study joint degenerative diseases
Karperien’s lab of Developmental Bioengineering: https://www.utwente.nl/en/tnw/dbe/
Le Gac’s lab of Applied Microfluidics for BioEngineering Research: http://www.severinelegac.com/
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/carlo-alberto-paggi-76500b135/

TPI.tv videos
InnovationPolicyBeginner
TPI.tv: improving science through animal-free innovations and research
Introducing TPI.tv : a video platform by experts striving to improve science through animal-free innovations and research.

Innovation examples
In vitroOrgan-on-Chip
Unified organoid system for modeling heart and kidney interaction on-a-chip
Beatrice Gabbin is a PhD candidate at the Anatomy and Embryology Department of the Leiden University Medical Center. Her project is shared with the Nephrology Department and focusses on the study of the cardiorenal axis in vitro. Both heart and kidneys have vital functions in the human body and reciprocally influence each other’s behavior: pathological changes in one can damage the other. There are already multiple independent in vitro (human) models of heart and kidney, but none have so far captured their dynamic crosstalk. The aim of the project is therefore to develop a microfluidic system which can be used to study heart and kidney interaction in vitro. For this purpose, cardiac microtissues and kidney organoids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells are generated and loaded onto a 3D perfusion chip for their dynamic co-culture. This system enables the study the cardiac and kidney interaction with a high level of control. The validation of a unified organoid system will enable the investigation of diseases involving the two organs and their potential treatments. Read more via the link in the video and https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100818.

Expert interviews
HealthToxicology
Ecotoxicology explained - interview by TOXstreams
Toxicology is a complicated area where you have to figure out if a chemical is safe for the entire human population? Well, some researchers in this field go even beyond, and instead of studying the safety of substances on “just” people, they focus on any living being on the whole planet. In this TOXstreams interview ecotoxicologists Dr Adam Lillicrap from the Norwegian Institute for Water Research and Dr Kristin Schirmer from the Eawag Science and Technology and co-founder of aQuaTox Solutions GmbH Solutions will explain what and how they do this. Click on the link in the video to watch the whole interview.

Innovation examples
HealthToxicologyIn silico
AI agents for safer science: How AI is Changing Chemical Risk Assessment
This video introduces a novel approach to chemical safety, where intelligent digital agents guided by large language models support scientists in making faster, more transparent decisions. By automating complex workflows and integrating tools like the OECD QSAR Toolbox, these agentic systems help prioritise research, reduce reliance on animal testing, and pave the way for safer, more sustainable innovation.

Innovation examples
EducationInnovation
Avatar Zoo - teaching animal anatomy using virtual reality
Animals are essential to train the next generation of scientists understand diseases and develop treatments for humans as well as animals. Therefore, animals are used for educational purposes. Technologies such as Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality can be employed to reduce the number of animals in the future. Prof. Dr. Daniela Salvatori is working on the development of 'Avatar Zoo' together with UMCU and IT. Live animals are replaced by holographic 3D in this flexible platform. With these holograms one is able to study the anatomical, physiological and pathological systems and processes of all kinds of animals.
Avatar Zoo won the Venture Challenge 2021 for the development of virtual reality models that can be used for anatomy classes and practical training.

Innovation examples
HealthToxicologyIn vitro
Assessing respiratory toxicity using in vitro models
The airways form a barrier for inhaled compounds, however, such compounds may cause local effects in the airways or may lead to lung diseases, such as fibrosis or COPD. Cell models of the respiratory tract, cultured at the air-liquid-interface (ALI) are a relevant model to assess the effects of inhaled compounds on the airways. Such models allow human relevant exposure, which is via the air, and assessment of effects on the epithelial cell layer. At RIVM we use air-liquid-interface cultured cell models and expose these to airborne compounds to assess the effects of agents such as nanomaterials, air pollutants or compounds from cigarette smoke. By using a mechanism-based approach to assess the effects of these compounds we invest in animal-free alternatives that better predict adverse effects in humans.

Projects and initiatives
HealthInnovationIn vitro
VitalTissue: scientific research can be more human(e)
The goal of VitalTissue is to facilitate the availability of vital human residual tissue for all researchers in the Netherlands. This video shows how VitalTissue works. From a request from a researcher, the donation of the residual tissue by the patient and the transport to the lab. This process is the result of a feasibility study conducted with many stakeholders. The national tissue bank ETB-BISLIFE will implement VitalTissue in practice.