In vitro

Projects and initiatives
HealthToxicologyIn vitroIn silico
VHP4Safety project
The safety testing of chemicals and pharmaceuticals traditionally relies on animal studies. However, these raise ethical concerns and often fail to accurately predict human responses. New scientific developments offer opportunities to build a Virtual Human Platform (VHP) for safety assessment, a platform that enables assessment based solely on human physiology and biology, integrating data from in vitro and in silico models. This video explains how we are developing the VHP through an interdisciplinary approach. Read the paper in the videolink or visit or VHP4Safety (https://vhp4safety.nl/) for more information.

Projects and initiatives
HealthIn vitroOrgan-on-Chip
NXTGEN Hightech Biomed
The Netherlands has strong academic knowledge in areas like Lab-on-Chip, Organ-on-Chip, artificial organs, and cell production technology. However, turning this knowledge into actual products is challenging due to the need for collaboration between different technological and biological specialists. The NXTGEN Hightech program (https://nxtgenhightech.nl/en/biomed/) addresses this by creating a collaborative environment where companies from various fields work together. This approach aims to transform academic insights into innovative products, benefiting both the industry and society.

Innovation examples
HealthToxicologyIn vitro
Thyroid Hormone & Brain Development: animal-free models for human safety assessment
The environment can have a significant impact on a child's health even before birth. Brain development begins in the first trimester and continues until the age of 25, with thyroid hormone playing a critical role. During early pregnancy, the fetus depends on the mother's thyroid hormone, and a disruption in the thyroid hormone balance can lead to cognitive and motor impairments in the child. As part of the VHP4Safety project, we are developing in vitro tests to measure the developmental neurotoxic effects caused by disturbances thyroid hormone concentrations. Current testing guidelines do not always include testing for neurodevelopmental effects, highlighting the need for new non-animal methods. At the Erasmus Medical Center, human cell lines representing brain cell types are cultured to study the effect of chemicals on the thyroid hormone balance. RIVM uses human stem cells to create neuron-astrocyte networks that mimic brain development. By combining these different assays and models, we are creating a comprehensive human-based testing strategy to assess developmental neurotoxicity. These advances are a critical step toward eliminating animal testing while protecting the health and environment of future generations.

Projects and initiatives
HealthToxicologyIn vitro
RISKHUNT3R project – interview by TOXstreams
Many studies are focused on finding the next best tool or test to assess the risk associated with chemical exposure. That is all well and good, but even the perfect assay needs to be accepted by regulators before seeing the light of the day. And how do we do that? The guests in this webinar have some ideas on that as principal investigators of the EU project RISK HUNT3R. Prof. Bob van de Water, Dr Mirjam Luijten and Dr Andrew White explain what RISK HUNT3R is doing, what next generation risk assessment means and why it is so important. Click on the link in the video to watch the whole interview.

Projects and initiatives
HealthToxicologyIn vitro
PrecisionTox project – interview by TOXstreams
What do nematodes, zooplanktons, clawed frogs, fruit flies, zebrafishes and humans have in common? Well, they are all part of the EU-funded project PrecisionTox. In this teaser for the TOXstreams interview, PrecisionTox researchers explain how they are combining non-traditional test species with molecular and computational methods to better protect our society from toxic chemicals. Prof. John Colbourne, the project’s coordinator, Dr Gaëlle Hayot, Christina Cramer von Clausbruch will tell all you want to know. Click on the link in the video to watch the whole interview.

Projects and initiatives
HealthToxicologyIn vitro
ONTOX project – interview by TOXstreams
Have you ever wondered how one can actually develop a new approach method (NAM) to replace animal testing in toxicology? The ONTOX project is creating not just one but six different NAMs. Indeed, this EU-funded project is focused on building NAMs to study repeated dose toxicity effects, an area of toxicology that still relies heavily on animal testing. Prof. Mathieu Vinken, the project’s coordinator, Jian Jiang, PhD, Anouk Verhoeven and Jonas van Ertvelde explain their work to TOXstreams. Click on the link in the video to watch the full episode.

Innovation examples
HealthIn vitro
Cultured human skin for burn research
Burns are often accompanied by a dysregulated immune response, which can lead to systemic inflammation, impaired immunity, and excessive scarring. A deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind burns—where wound healing and inflammatory reactions are severely disrupted—holds the key to improving patient outcomes. Patrick Mulder, a postdoctoral researcher at the Burn Research Lab in Beverwijk, the Netherlands, works with his colleagues to develop animal-free skin models based on human cells and patient-derived tissues. Using these innovative, human-relevant models, he aims to provide greater insight into the body’s response to burns and studies the effects of existing and new treatments on wound healing.
Click on the info button for the full version of the video.

Innovation examples
HealthIn vitroOrgan-on-Chip
An iPSC-derived blood-brain barrier to model neurodegeneration
The blood-brain barrier is a layer of cells that protects our brain from harmful compounds. However, due to this tight barrier, many drugs to treat neurological diseases cannot enter the brain either.
There are currently no good models to test these types of drugs. Henrique Nogueira Pinto is a PhD candidate at the Vrije Universiteit in Amsterdam. He is developing a blood-brain barrier model coupled to mini-brains. With this model, he aims to more reliably test how drugs can be transported over the blood-brain barrier and what their effect on the brain is.
Click on the info button for the full version of the video. Click here (https://fluidsbarrierscns.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12987-022-00316-0#Sec3) for a review of the current status of in vitro models for the blood-brain barrier.

Innovation examples
HealthIn vitro
Organoids for studying (personalised) antiviral treatments
Giulia is a scientist in clinical virology with a PhD from OrganoVIR Labs at Amsterdam UMC. Her research aims to improve antiviral testing using human organoids—tiny, lab-grown tissues that mimic real human organs. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the urgent need for effective antiviral treatments, as traditional pre-clinical testing on animal models has only a 5% success rate in clinical trials. By utilising human organoids, Giulia enhances the accuracy of antiviral research. She specializes in infecting organoids from the airway, gut, and brain with various patient-derived viruses, allowing for more realistic modelling of viral infections. Her work also sets the stage for personalised medicine in the context of viral infections. By isolating viruses and stem cells from patients suffering from severe infections, she can test tailored treatments that are more likely to succeed. With this, she aims to revolutionise antiviral testing and improve treatment outcomes for patients.
Click on the info button for the full version of the video.

Projects and initiatives
HealthIn vitro
CONNECT
Many people worldwide suffer from brain diseases. These diseases are often hard or even impossible to treat. One of the reasons for this that potentially beneficial drugs cannot pass through the blood-brain barrier. The CONNECT project aims to develop a blood-brain barrier model and connect this to a brain model, all derived from cells. With this advanced in vitro test system, researchers aim to be able to study how drugs can be transferred more effectively and safely over the blood-brain barrier in an animal-free and human-relevant manner.

Innovation examples
ToxicologyIn vitro
Combatting the worlds deadliest infections using groundbreaking human-mimetic tools
Combatting the worlds deadliest infections using groundbreaking human-mimetic tools.
Zika, dengue & other viruses are typically tested in monkeys & mice. But is using animals really the most effective way? Find out what Dr. David Pamies of the @jhucaat - along with his colleagues at @JohnsHopkins - are doing to upend the status quo.
More information on:
https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2019-06/hsi-ctw061319.php
and
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2019.00223/
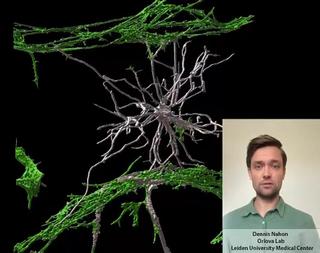
Innovation examples
HealthIn vitroOrgan-on-Chip
Stem cell derived Vessels-on-Chip to study brain disorders
Dennis Nahon is a PhD candidate in the Department of Anatomy and Embryology at the Leiden University Medical Center. In his research, under supervision of Dr. Valeria Orlova (https://www.orlovalab.com/) and Prof. Dr. Christine Mummery, he aims to mimic a blood vessel in the brain by combining different stem cell derived cell types, in a 3D Vessel-on-Chip model. Here, an example of these in vitro blood vessels is shown in which certain brain cells known as astrocytes (in white) interact with the blood vessels (in red). This model paves the way for investigating brain vessels outside the human body, while reducing the need for animal models.